In the world of technology, digital documents and transactions are standard. However, there is a significant problem: electronic documents are more prone to security risks than their paper counterparts. That’s why an eSignature is important as a mathematical way of validating information and preventing data theft. Let’s look at a digital signature in cybersecurity. How can it protect a company?
Contents
Is a digital signature the same as its handwritten counterpart?
Before the advent of the Internet era, people needed to use a seal or a handwritten signature to prove the authenticity of important information. Now, a user can send any file online, and the recipient will know the owner due to their unique “virtual fingerprint” – a digital signature.
A digital signature in cybersecurity is a kind of eSignature based on a mathematical algorithm. It allows you to make sure that the transmitted information is genuine and complete (for example, an email, payment by electronic card, electronic document, website, or other electronic assets).
A digital signature assures a recipient of a document that:
- data came from a legitimate person, not from a cybercriminal;
- a document, letter, or other data is signed by the owner of the digital signature, not by someone else;
- no one falsified the data during transmission.
The application of a digital signature can be compared to one of the standard tasks a notary performs. This expert confirms the identity of an owner and the authenticity of their signature. After the notary sets their seal on a document, it acquires legal status. Other authorities can use the document for legitimate transactions only after notarization has been carried out.

What makes a digital signature secure?
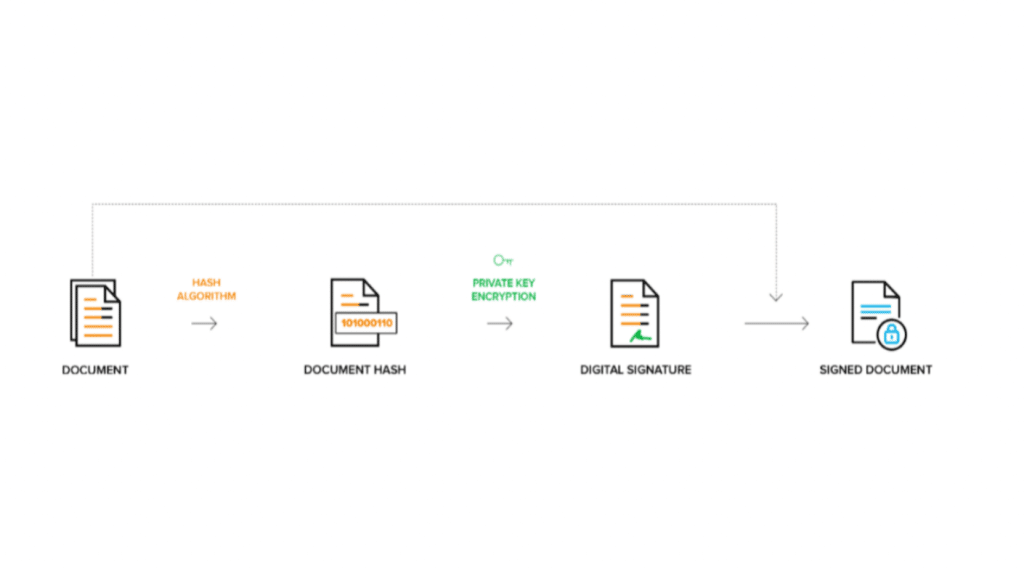
A digital signature is a secure eSignature type. It has an enhanced sd wan security mechanism. Briefly, it can be described as follows. When the owner of a document signs it, the content of the file is hashed and encrypted with the SHA-1, SHA-2, or other algorithms. When creating a digital signature, a pair of interrelated keys is generated (public and private). They are strongly linked to each other because only the public key can decrypt the data encoded with the private one.
Like any security mechanism, a digital signature has its own rules and regulations. A PKI is responsible for the distribution of public keys and the identification of individuals and legal entities. It is a special infrastructure that combines rules, people, and systems into one. The relationship between the key pair is maintained by certificate authorities. In turn, digital certificates provide complete information about the owner of a digital signature (like a driver’s license or passport).
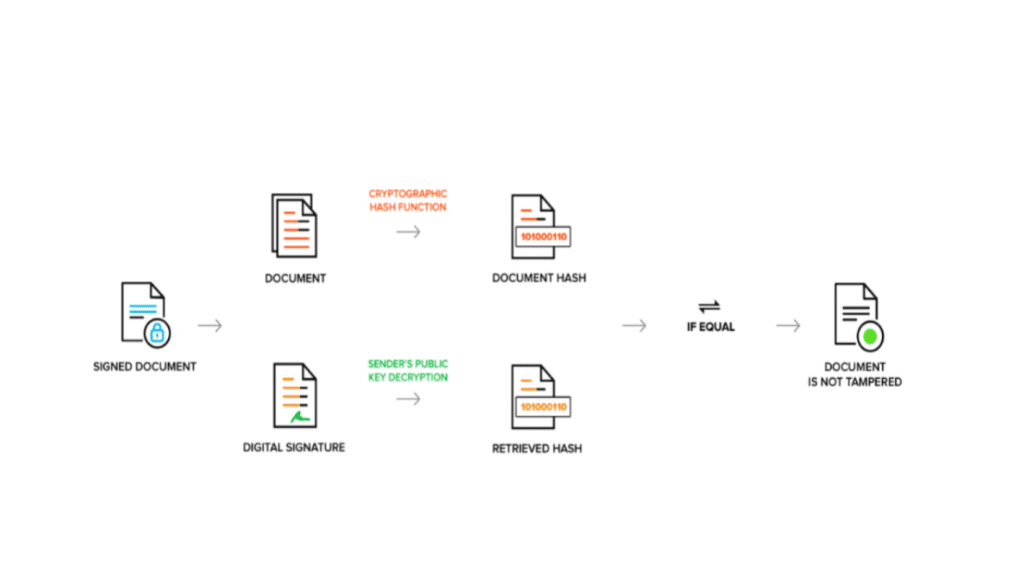
When a recipient opens a message, they decrypt the sender’s digital signature with the public key. Their computer compares the original hash with the hash of the incoming message. If they match, it means that the document is authentic and can be processed. A hash mismatch is a sure sign that the document has been compromised.
The introduction of a digital signature as a step to strengthen the protection of an organization
Security is the main advantage of digital signatures. Organizations should use this benefit to strengthen their cyber defense. On the one hand, a digital signature can protect emails, documents, software, and other assets. On the other hand, it protects people. By implementing it into the workflow, a business can:
- reduce phishing and data theft incidents. When company employees digitally sign emails, their colleagues will be less likely to open messages from unfamiliar sources. For an organization, this move means fewer hacks and data privacy threats.
- improve communication security. Digital signatures provide trust between different parties. Enterprises should implement a mechanism for verification of the authenticity of business documents, data, and messages to avoid falsification. With the help of a digital signature, an employee can easily sign documents on their smartphone, computer, or tablet.
- reduce costs. According to IBM, it takes an average of $4.35 million to fix a data breach. The use of a digital signature can reduce costs and penalties for non-compliance with the law. Organizations will also spend fewer resources managing and storing paper documents. A manager can be located in any geographic region, get access to records promptly, and sign them.
- comply with safety regulations. The PKI standard guarantees the secure generation and storage of keys. More and more countries are recognizing digital signatures as legally binding. In the USA, there are UETA and ESIGN regulations. The European Union has eIDAS. Accordingly, companies supporting eSignatures comply with security requirements.
Conclusion
A digital signature can enhance the protection of data, products, or services of any business – be it a custom software development, a bank, or a logistics company. This cryptographic tool is convenient as it encourages remote communication and collaboration. It helps reduce the cost of combating cyberattacks and ensures compliance with international laws. It becomes an undeniable advantage in organizations where safety is paramount.